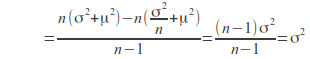The number of degrees of freedom is the number of values in thefinal calculation of a statistic that are free to vary.
A simple example is shown in calculating the mean of a sample.Suppose![]() isa sample from a population.
isa sample from a population.
Let![]()
The![]() areestimates of the residuals
areestimates of the residuals![]() where
where![]() isthe true mean of the population.
isthe true mean of the population.
The sum of the residuals (unlike the sum of the errors) isnecessarily 0. If we know the values of any![]() ofthe residuals, we can find the last residual, so that even thoughthere are n residuals, only
ofthe residuals, we can find the last residual, so that even thoughthere are n residuals, only![]() ofthese are free to vary. For this reason we say that the residuals ofa sample of size n has
ofthese are free to vary. For this reason we say that the residuals ofa sample of size n has![]() degreesof freedom.
degreesof freedom.
For the same reason, the sample standard deviation![]() includesan expression n-1 in the denominator.
includesan expression n-1 in the denominator.
We can write![]()
![]() isthe sum of the squares of the residuals and the residuals only haven-1 degrees of freedom, so that
isthe sum of the squares of the residuals and the residuals only haven-1 degrees of freedom, so that
![]()
![]()
![]()