Apparatus:
Free fall apparatus consisting of two sets of light gates, ball bearing and batteries, timer.
Diagram:
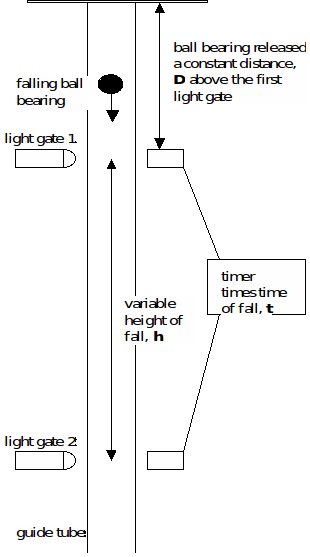
Procedure:
1. The apparatus should be mostly set up already as shown in the diagram. However, you will need to connect the timer to the light gates and align these gates. If the set up is correct, then as the falling mass passes through the first gate the timer should start and when the mass passes through the second gate the timer should stop. In each case the mass interrupts the light beam at the gates. the timer will read time,![]() to ± 0.01 second. The upper gate is fixed in position a distance
to ± 0.01 second. The upper gate is fixed in position a distance![]() from the top of the apparatus.
from the top of the apparatus.
2. The lower light gate should be positioned initially about 55 cm below the upper gate, measure this distance,![]()
3. Allow the mass to fall from the top of the guide tube and so obtain a time for the fall between the two light gates. Repeat twice more and so obtain a mean value of![]() to three significant figures.
to three significant figures.
4. Repeat stage 4 for seven further different distances of fall,![]() between 55 cm and 120 cm.
between 55 cm and 120 cm.
Theory, Graph and Calculation:
Throughout the fall through distance,![]() the acceleration is assumed to be constant and equal to
the acceleration is assumed to be constant and equal to![]() the acceleration due to gravity. The velocity at the first light gate equals
the acceleration due to gravity. The velocity at the first light gate equals![]() and that at the second equals
and that at the second equals![]() with time of fall equal to
with time of fall equal to![]()
Then![]() becomes
becomes![]()
Also![]() becomes
becomes![]() but
but![]() therefore:
therefore:![]()
and so![]() which we can write as
which we can write as![]()
This equation has form![]() so if a graph of
so if a graph of![]() is plotted on the
is plotted on the![]() - axis against
- axis against![]() on the
on the![]() - axis it should be a straight line of gradient
- axis it should be a straight line of gradient![]()
Plot this graph and hence determine![]()