Apparatus:
Capillary tube with mercury, ruler, plumb line, metre ruler and clamp stand.
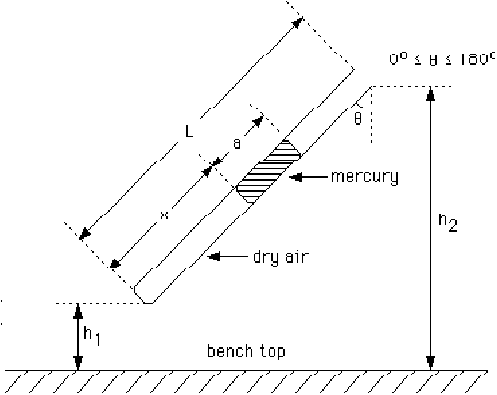
Procedure:
1. Measure the length of the air column,![]() (in mm) as a function of
(in mm) as a function of![]() from
from![]() = 0 to
= 0 to![]() = 180 .
= 180 .![]() can be found by measuring (with the aid of a metre rule and the plumbline)
can be found by measuring (with the aid of a metre rule and the plumbline)![]() and
and![]() as defined in the diagram above (Do not use a protractor).
as defined in the diagram above (Do not use a protractor).
2. Measure the length of the mercury index, a (in mm) .
3. Draw a graph of![]() (in
(in![]() )against
)against![]() and hence use it to find the atmospheric
and hence use it to find the atmospheric
pressure![]() (in mm of mercury). (See below for theory).
(in mm of mercury). (See below for theory).
4. Compare the value of atmospheric pressure found by using this method with the value measured using the Fortin barometer in the corridor.
Theory : From Boyle's Law![]() with
with![]() mm of mercury
mm of mercury
and![]() [
[![]() and
and![]() are constants].
are constants].
Boyle's law become![]() [
[![]() is another constant]
is another constant]
therefore![]() and so
and so![]()
leaving![]()
Compare this with the equation of a straight line![]()
Measure (or calculate) the gradient,![]() and the
and the![]() - intercept,
- intercept,![]()
And so find![]() where
where![]()