Apparatus:
Two metre rulers (one thinner than the other), 1kg load, string, two pivots, two wooden blocks for the pivots, set square.
Diagram:
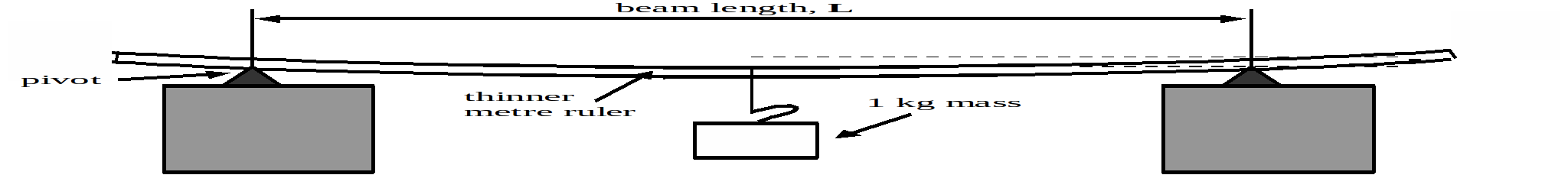
Procedure:
1. Set up the apparatus as shown in the diagram above. The thinner metre ruler should be placed so that the pivots lie below the 100 and 900mm marks. The 1kg mass should hang from the 500mm point. This will mean that the length of the ruler,![]() between the pivots is 0.800m
between the pivots is 0.800m
2. Use the other metre metre to measure the sag,![]() of the thinner metre ruler caused by the 1kg mass. You should attempt to do this more than once.
of the thinner metre ruler caused by the 1kg mass. You should attempt to do this more than once.
3. Repeat the above for five more values of![]() between 0.500m and 0.900m. In all cases the 1kg mass should hang from the mid-point between the pivots.
between 0.500m and 0.900m. In all cases the 1kg mass should hang from the mid-point between the pivots.
4. For each value of L calculate:
(a)![]() &
&
(b)![]()
5. Draw a graph of![]() against
against![]()
6. From this graph, using the theory shown below, confirm, or otherwise, that the relationship between the sag,![]() and the beam length,
and the beam length,![]() is given by
is given by![]()
7. Explain how you measured the sag,![]() of the ruler.
of the ruler.
Theory:
Let![]()
Taking logs on both sides gives![]()
which can be rearranged into![]()
This equation has the form of a straight line, that is![]()
In this case the![]() term corresponds to
term corresponds to![]() and the
and the![]() term to
term to![]() The gradient of your graph will be n so you can find the value of
The gradient of your graph will be n so you can find the value of![]() in the relationship
in the relationship![]()