Solving Second Order Constant Coefficient Linear Differential Equations
A second order constant coefficient linear differential equation is any equation of the form
![]() where
where![]() and
and![]() are constants. Solving these involves
are constants. Solving these involves
Finding a solution
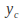 of the homogeneous equation
of the homogeneous equation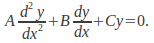 We may assume a solution of the form
We may assume a solution of the form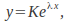 obtaining the 'characteristic' equation
obtaining the 'characteristic' equation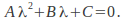 If this equation has two distinct real roots
If this equation has two distinct real roots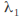 and
and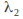 then
then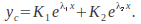 If the equation has a single repeated root
If the equation has a single repeated root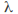 then
then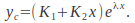 If the equation has complex roots
If the equation has complex roots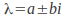 then
then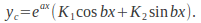
Now find a particular solution
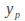 of the inhomogeneous equation
of the inhomogeneous equation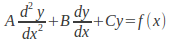 by assuming a solution similar to the function
by assuming a solution similar to the function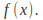 For example if
For example if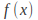 is a polynomial of degree
is a polynomial of degree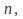 then assume
then assume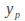 is also a polynomial of degree
is also a polynomial of degree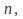 so that if
so that if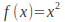 then assume
then assume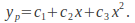 The constants
The constants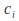 can be found by equating coefficients.
can be found by equating coefficients.The general solution is the sum of the complementary and particular solutions:
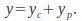 The constants
The constants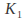 and
and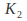 can be found if we are given two conditions on
can be found if we are given two conditions on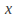 and
and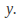
Example: Solve the equation![]() if
if![]() and
and![]() at
at![]()
Assuming a solution to the homogeneous equation![]() of the form
of the form![]() we have
we have![]() and
and![]() The equation becomes
The equation becomes![]()
The complementary solution is then![]()
Assume a particular solution of the form![]() and
and![]() so the equation becomes
so the equation becomes![]()
Equation coefficients of![]() gives
gives![]() Equating constants gives
Equating constants gives![]() The particular solution is then
The particular solution is then![]() We have
We have![]()
The first condition![]() gives
gives![]()
![]()
The second condition gives![]()
The solution to the problem is![]()