Simultaneous equations involve at least two unknown that must be found. If we have two equations and two unknowns or three equations and three unknowns then we can generally solve the equations. Typically the two unknowns are labelled![]() and
and![]() as in the following simultaneous equations.
as in the following simultaneous equations.
![]() (1)
(1)
![]() (2)
(2)
The procedure for solving simultaneous equations is:
-
Choose
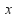 or
or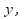 and make the size of the coefficients of
and make the size of the coefficients of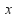 or
or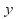 the same. In the above equations the coefficients of
the same. In the above equations the coefficients of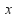 are 2 and 3, and the coefficients of
are 2 and 3, and the coefficients of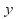 are 1 and 2. We can make the coefficients of
are 1 and 2. We can make the coefficients of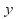 the same by multiplying (1) by 2, then both equations have
the same by multiplying (1) by 2, then both equations have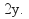 The new equations are
The new equations are
![]() (3)
(3)
![]() (2)
(2)
-
We can now eliminate the
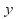 terms by subtracting:
terms by subtracting: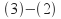 gives
gives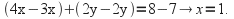
-
Now find
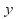 by substituting this value for
by substituting this value for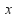 back into one of the equations (1) or (2) and solve to find
back into one of the equations (1) or (2) and solve to find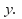
Suppose we substitute![]() into
into![]()
Example: Solve the simultaneous equations
![]() (4)
(4)
![]() (5)
(5)
We can make the![]() coefficients the same size by multiplying (4) by 2 and multiplying (5) by 3. This will result in them being the same size but having opposite sign. We do not subtract – we add to eliminate the
coefficients the same size by multiplying (4) by 2 and multiplying (5) by 3. This will result in them being the same size but having opposite sign. We do not subtract – we add to eliminate the![]() - terms.
- terms.
![]() (6)
(6)
![]() (7)
(7)
(6)+(7) gives![]()
Substitute![]() into (4) to obtain
into (4) to obtain![]()