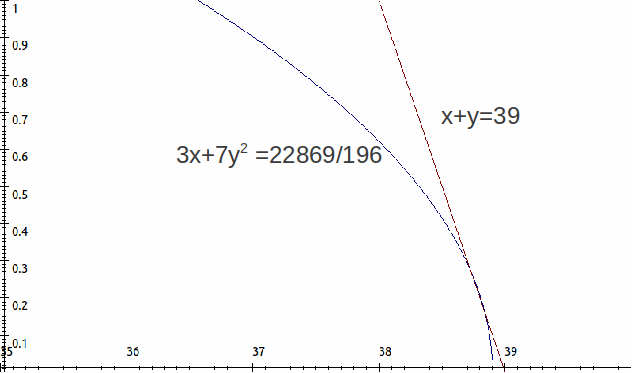Lagrange multipliers are used in optimising or maximising a function![]() subject to one or more equality constraints
subject to one or more equality constraints![]() The solution is found by minimizing
The solution is found by minimizing![]() with respect to the
with respect to the![]() and
and![]() The Lagrange multipliers are the
The Lagrange multipliers are the![]()
For example to maximise![]() subject to
subject to![]() form the expression
form the expression![]()
Differentiating with respect to![]() gives
gives![]() (1)
(1)
Differentiating with respect to![]() gives
gives![]() (2)
(2)
Differentiating with respect to![]() gives
gives![]() (3)
(3)
From (1)![]()
From (2)![]()
From (3)![]()
The maximum value of![]() is then
is then![]()
This is illustrated below. The maximum is where the curves touch.