Define the projection of the point![]() onto the real
onto the real![]() and
and![]() axes respectively as
axes respectively as
![]()
![]()
Consider the inverse function![]() If
If![]() acts on an open interval
acts on an open interval![]() the result is a vertical strip with
the result is a vertical strip with![]()
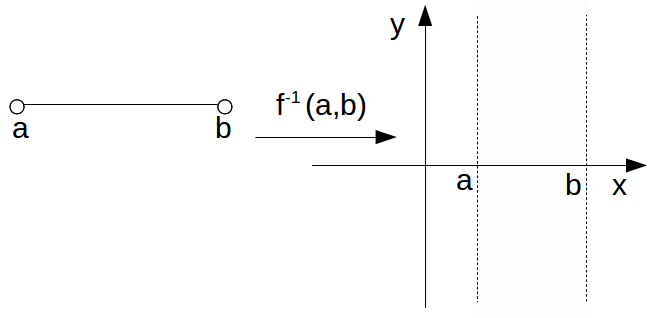
The set of open intervals is a basis for![]() and the inverse image of each open interval is an open strip as above. These open strips are open in
and the inverse image of each open interval is an open strip as above. These open strips are open in![]() so
so![]() is continuous, and similarly for
is continuous, and similarly for![]()