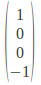The Stokes Vector
The Stokes vector represents a polarized wave in terms of four 'Stokes parameters'. The Stokes parameters of a light wave are measurable quantities defined as
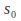 – Total flux density.
– Total flux density.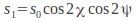 – The difference between the flux density transmitted by a linear polarizer oriented parallel to the x – axis and one oriented parallel to the y – axis. The x and y axes are usually selected to be parallel to the horizontal and vertical axes in the laboratory.
– The difference between the flux density transmitted by a linear polarizer oriented parallel to the x – axis and one oriented parallel to the y – axis. The x and y axes are usually selected to be parallel to the horizontal and vertical axes in the laboratory.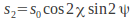 – The difference between the flux density transmitted by a linear polarizer oriented at 45 Degrees to the x axis and one oriented at 135 Degrees.
– The difference between the flux density transmitted by a linear polarizer oriented at 45 Degrees to the x axis and one oriented at 135 Degrees.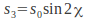 – The difference between the flux density transmitted by a right circular polarizer and a left circular polarizer.
– The difference between the flux density transmitted by a right circular polarizer and a left circular polarizer.These are illustrated below:
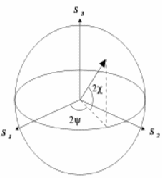
The Stokes vector may be written in vector form, for example:
Horizontal Polarization:
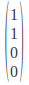
Vertical Polarization:
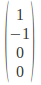
+45 Degrees Polarization:
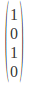
-45 Degrees Polarization:
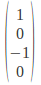
Right Circular Polarization:
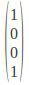
Left Circular Polarization: