Apparatus:
Dynamics trolley, runway, clamp stand etc., 2 x metre rulers, top-pan balance, set-square & stop-clock.
Diagram:
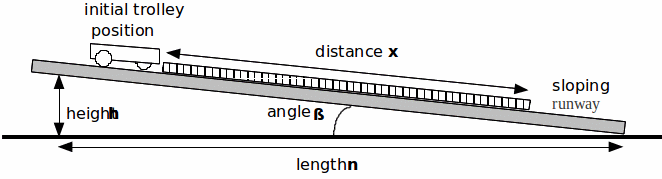
Procedure:
1. Clamp the runway in such a way that the dynamics trolley takes time,![]() to roll, from rest, distance
to roll, from rest, distance![]() down the runway.
down the runway.
2. Measure this time,![]() three times. Calculate the average value of t.
three times. Calculate the average value of t.
3. In order to determine the angle of slope of the runway![]() measure height
measure height![]() and length
and length![]() Length
Length![]() should be at least 70 cm. Calculate
should be at least 70 cm. Calculate![]()
4. Calculate the acceleration![]() f the trolley by using
f the trolley by using![]()
(If the trolley starts from rest, then![]() ).
).
5. Repeat for four more different angles![]() with the time
with the time![]() varying between about 1 and 5 seconds.
varying between about 1 and 5 seconds.
6. Tabulate your results.
7. Measure the mass M of the dynamics trolley.
8. Plot a graph of acceleration a (in m/s 2 ) against![]()
Ensure that your acceleration scale goes down to at least minus 0.2 m/s 2 .
Draw a best fit curve. Your graph should gently curve with a negative intercept on the acceleration axis.
9. Use your graph to find the angle![]() of the runway when it is "frictionless" (i.e. when the acceleration of the trolley would be zero).
of the runway when it is "frictionless" (i.e. when the acceleration of the trolley would be zero).
10. Draw a tangent to your line at the point where the acceleration is zero. Calculate the gradient![]() of this tangent.
of this tangent.
11. Record the value of the intercept![]() on the acceleration axis.
on the acceleration axis.
12. Calculate the frictional force,![]() acting on the trolley at low accelerations given that:
acting on the trolley at low accelerations given that:
![]()
13. Why is the above method of measuring angle![]() better than using a protractor?
better than using a protractor?
