The Casimir effectgives rise to a force between close parallel uncharged conducting plates and arises from quantum vacuum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field.
According to the quantum theory, the vacuum contains virtual particles which are in a continuous state of fluctuation. Casimir realised that between two plates, only those virtual photons whose wavelengths fit a whole number of times into the gap should be counted when calculating the vacuum energy.
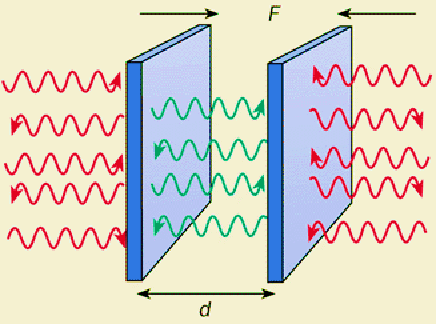
The energy density decreases as the plates are moved closer, which implies that there is a small force drawing them together.
The attractive Casimir force between two plates of area![]() separated by a distance
separated by a distance![]() can be calculated to be,
can be calculated to be,
where![]() is Planck's constant and
is Planck's constant and![]() is the speed of light.
is the speed of light.
Since![]() is in the denominator, the bigger
is in the denominator, the bigger![]() gets, the smaller the force will be; and because the force goes as the fourth power of
gets, the smaller the force will be; and because the force goes as the fourth power of![]() the force decreases rapidly with increasing
the force decreases rapidly with increasing![]() Suppose
Suppose![]() and
and ![]()
![]()
