When light is shone on a metal surface, electrons may be emitted from the surface. Sometimes electrons are emitted, sometimes not. It depends on the energy, hence the frequency,![]() of the incident light.
of the incident light.
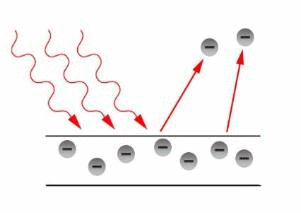
In the diagram, light enters from the top left. It hits the metal plate. The photons of light on the left and have enough energy to eject a photon from the metal plate, but the photon in the centre does not.
The equation governing the photoelectric effect is![]() (1) where
(1) where
![]() is the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electrons for a certain frequency of light
is the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electrons for a certain frequency of light
![]() is Planck's constant,
is Planck's constant,![]()
![]() is the frequency of the incident light in Hz
is the frequency of the incident light in Hz
![]() is the work function of the metal, the minimum amount of energy needed for a photon to escape from the metal surface.
is the work function of the metal, the minimum amount of energy needed for a photon to escape from the metal surface.
For light above a certain frequency, called the threshold frequency, light will be emitted. We can find this frequency from (1). Since the maximum kinetic energy of the ejected electron,![]() we must have from (1)
we must have from (1)![]() That value of v for which
That value of v for which![]() or
or![]() is called the threshold frequency,
is called the threshold frequency,![]() , and below this frequency no electron emission takes place.
, and below this frequency no electron emission takes place.
The Work Function and the Stopping Potential
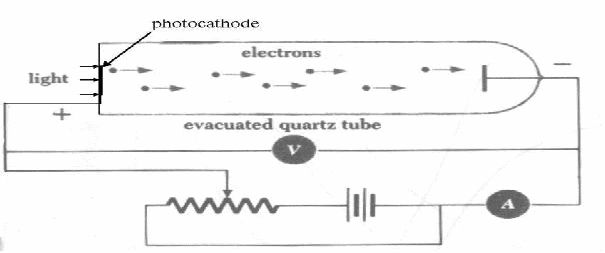
Electrons are emitted from the photocathode and move towards the negatively charged plate. Because it is negatively charged, the electrons are repelled from it and slow down. If we vary the voltage, we can find the voltage which just stops the electrons reaching the negative plate and producing a current. In travelling towards the plate, all the original kinetic energy will be translated into potential energy of the field eV so 1 over![]() , so we can find the work function of the metal of which the cathode is made using
, so we can find the work function of the metal of which the cathode is made using![]()
Finding Planck's Constant
Equation (2) can be rearranged in the form![]()
We can measure f and V and plot a graph of f against V. The gradient of this graph will be![]()
