The basic relationship that expresses random decay as a random process is sxpressed mathematically as![]() where N is the number of undecayed atoms remaining.
where N is the number of undecayed atoms remaining.
The constant of proportionality is negative since N is decreasing so dN < 0. We may write![]() where
where![]() is the number of decays in each time period
is the number of decays in each time period![]() typically taken to be 1 second, and
typically taken to be 1 second, and![]() is a positive constant called the decay constant. The proportion of atoms that will decay in a time dt or probability that an individual atom will decay in a time
is a positive constant called the decay constant. The proportion of atoms that will decay in a time dt or probability that an individual atom will decay in a time![]() is then
is then![]()
We can solve the equation![]() obtaining
obtaining![]() where N-0 is the number of undecayed atoms initially present. A similar expression exists for the activity
where N-0 is the number of undecayed atoms initially present. A similar expression exists for the activity![]()
We can find the decay constant %lambda in the following way.
Take natural logarithms of![]() obtaining
obtaining![]() This is the equation of a straight line graph, with
This is the equation of a straight line graph, with![]() on the vertical axis and gradient
on the vertical axis and gradient![]()
A graph of N against t is shown below. The number of undecayed atoms fall by a half in each fixed time period called the half life, labelled![]()
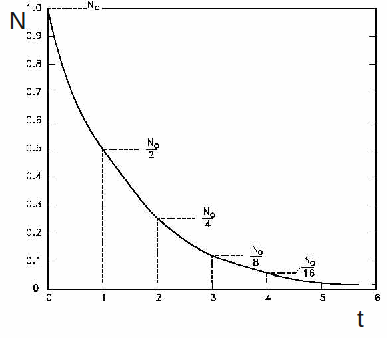
We can find the half life by substituting![]() and
and![]() into
into ![]()
![]()
Alternatively we could observe the time taken for the activity to decay by a half, but this is less accurate.
