The Earth spins on its axis once every twenty four hours, and moves around the Sun once every 365.25 days. It is tilted on its axis, so that as it moves around the Sun, at one point in its orbit, the North Pole is tilted towards the Sun and at another, when the Earth has moved halfway around the Sun, the South Pole is tilted towards the Sun.
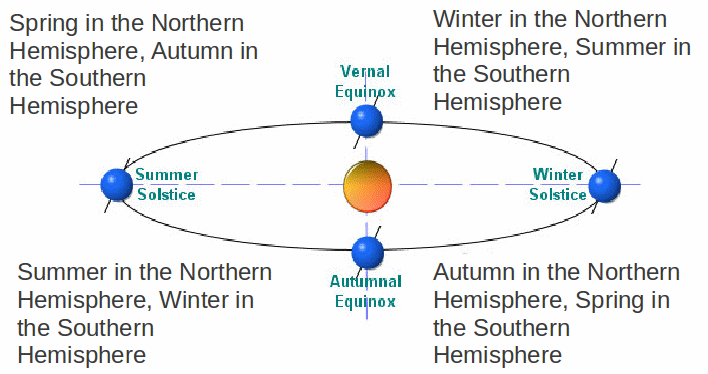
When the North Pole is tilted towards the Sun, the Sun appears higher in the sky in the Northern hemisphere, and the days last longer. The Northern hemisphere is then heated more, and is warmer. On the other hand, the Sun appears lower in the sky in the Southern hemisphere, and the days are shorter and colder. It is Summer in the Northern hemisphere and Winter in the Southern hemisphere.
Six months later the positions are reversed. The North Pole is tilted away from the Sun, the Sun appears lower in the sky in the Northern hemisphere, and the days are shorter. The Northern hemisphere is then heated less, and is colder. On the other hand, the Sun appears higher in the sky in the Southern hemisphere, and the days are longer and hotter. It is Winter in the Northern hemisphere and Summer in the Southern hemisphere.
The points of most tilts of the Earth's axis are called the solstices. In ancient times they were times of religious celebration and worship. Stonehenge in England was built with the solstices in mind.
