When constructing ray diagrams to find the position and nature of the image formed by a lens, we draw the paths followed by three rays. As soon as this is done, the paths followed by all other rays can be inferred. The rays whose paths are drawn are slightly different for converging and diverging lenses.
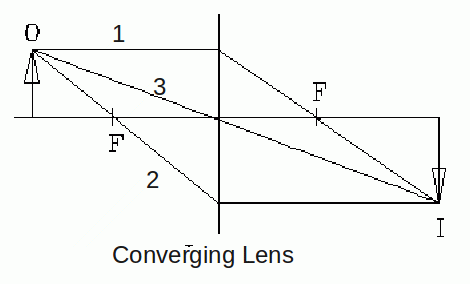
Converging Lenses
-
Any ray travelling parallel to the principal axis will be refracted and pass though the focal point after passing though the mirror.
-
Any ray passing through the focal point will be refracted and follow a path parallel to the principal axis.
-
Any ray passing through the centre of the lens will be undeviated.
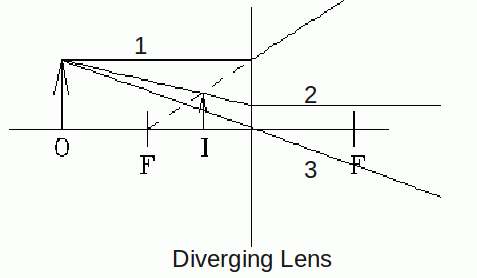
Diverging Lenses
-
Any ray travelling parallel to the principal axis will be refracted away from the principal axis, and will appear to have passed through the focal point when traced back
-
Any ray heading toward the focal point on the other side of the lens will be refracted and travel parallel to the principal axis after passing through the lens.
-
Any ray passing through the centre of the lens will be undeviated.
-
