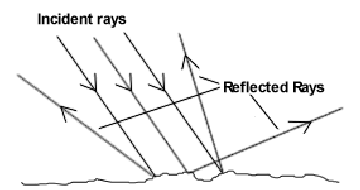
When a single ray of light strikes a mirror, it produces a single reflected ray.
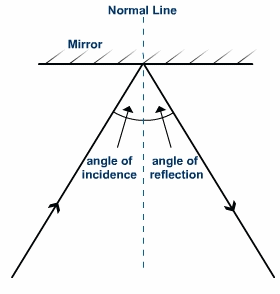
The angle of incidence – the angle between the normal line and the path traced by the incident ray is equal to the angle of reflection – the angle between the normal line and the path taken by the reflected ray. In addition, the incident and reflected rays and the normal all lie in the same plane.
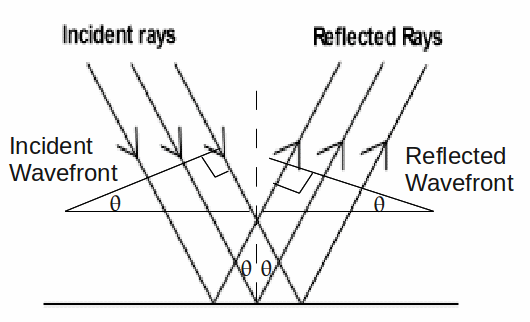
If a wavefront strikes a mirror, then the reflected wavefront makes the same angle with the mirror as the incident wavefront, and both angles are equal to the angle of incidence.
Many surfaces are not smooth like a mirror and light is reflected from them in all direction. This is called diffuse relection.