Refraction is the change in direction of a wave that takes place at the interface between two media. The speed and the wavelength of the wave will also change, but the frequency will not. When light passes from a less dense medium to a denser medium, as below, it will be refracted towards the normal (the broken vertical line below).
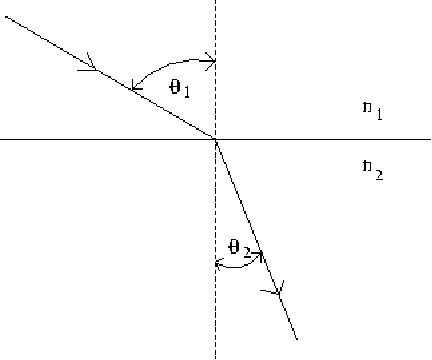
Snell's law gives us a relationship between the angle of incidence![]() and the angle of refraction
and the angle of refraction![]()
The refractive index of the vacuum is taken to be 1. The refractive index of air is so nearly equal to 1 that it is often taken to be 1. If media 1 above is air, and![]() is 30 degrees, and medai 2 is glass for which the refractive index is 1.4 then
is 30 degrees, and medai 2 is glass for which the refractive index is 1.4 then
![]()
Similar relationships hold for the wavelength:![]() and the speed
and the speed![]()
If the wavelength in medium 1 in the above example is 2 cm then![]() and
and![]()
The frequency is the same in both media.
