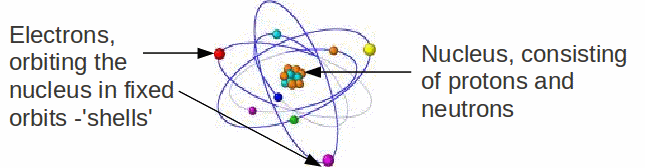
All the material around us is made up of atoms. Atoms of different 'types' – they have a different number of protons in the nucleus - are different elements. There are currently 117 different elements, which make up the periodic table, in which elements are ordered by the number of protons in the nucleus, which is called the atomic number.
Chemical Properties
Though the number of protons determines which element the atom is, the chemical properties of the atom are only an indirect effect of this. The chemical properties of the atom are a consequence of the electron arrangement of the electrons. The atom as a whole is neutral. Since the charges of electron and proton are equal and opposite in sign, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons. Chemical bonds are actually only formed between electrons, and the bond formed depends on how the electrons are arranged in the shells of each atom.
Notation
The symbol for an atom is![]() where:
where:
M is the mass or nucleon number of the atom, equal to the number of protons plus the number of neutrons.
Z is the atomic number, or the number of protons.
A is the symbol for the element, found in the periodic table eg U for Uranium.
This information may be summarised by![]()
Isotopes
The chemical properties of an element is determined (indirectly) by the number of protons. ONLY BY THE NUMBER OF PROTONS! Neutrons may contribute to the mass number but they do not affect an elements chemical properties. Two atoms with the same number of protons may have a different number of neutrons without changing any chemical properties at all. The two atoms will undergo the same chemical reactions, release or consume the same amount of energy when undergoing those reactions etc. Such atoms – with the same number of protons but differing numbers of neutrons – are called isotopes.
