The Newton Raphson Method is an iterative method for finding roots.
Suppose we know the rough location of a root![]() to a function
to a function![]() we know it is close to some value
we know it is close to some value![]() We can expand the function
We can expand the function![]() in a Taylor series about a value of
in a Taylor series about a value of![]() close to
close to![]()
Since![]() is close to 0 we can say
is close to 0 we can say
![]()
Generalizing we have![]()
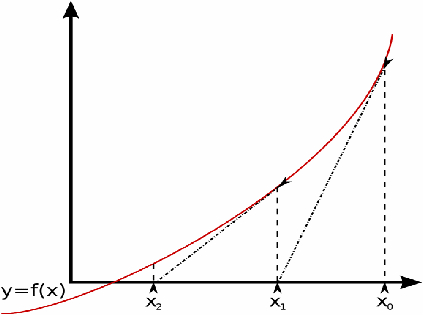
This is illustrated in the diagram below.
Each iteration gives a value closer to the true root, which is used in the next iteration to find a value closer to the true root.
Example: Find the root![]() of the equation
of the equation![]() starting from
starting from![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
We could go on but these two values agree to three decimal places, so to 3 decimal places,![]()
