If we have two independent populations with unknown variances, then we can use the t –distribution to test hypotheses about the means of the two populations – either that they are equal or that they differ by a certain amount. The procedure is:
-
Write down the null hypothesis
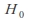 for example
for example or
or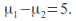
-
Write down the alternative hypothesis
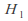 for example
for example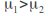 or
or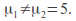
-
Specify the significance level
-
Write down the number of degrees of freedom
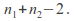
-
Write down the critical value (one tailed test), values (two tailed test) or the critical region (one tailed test) or critical regions (two tailed test).
-
Calculate the sample means
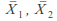 and variances,
and variances,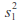 and
and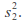
-
Calculated the pooled variance
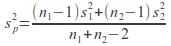
-
Calculate the value of the test statistic
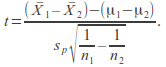
-
Interpret the statistic. If the value of the test statistic is in the critical region,
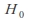 canbe rejected at the significance level of the test.
canbe rejected at the significance level of the test.
Example: Conduct a hypothesis test at the 10 % level for the equality of the means ofthe populations from which the following samples are drawn.
Population 1: 4, 2, 4, 8, 2,6
Population 2: 7, 3, 6, 1, 9,9, 10
For a significance level of10% with 6+7-2 =11 degrees of freedom, (we are conducting a two tailed test since we are testing for equality) the critical values are![]()
![]()
![]()
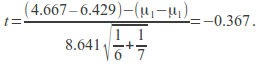
This is not in the critical region since![]()
