The accleration due to gravity is given by![]() where
where![]() is the Gravitational constant,
is the Gravitational constant,![]() is the mass of the Earth and
is the mass of the Earth and![]() is the radius of the earth. The formula above assumes a spherically uniform distribution of mass, this this assumption is only approximately true. The Earth is not a sphere, being flattened at the poles, nor is the density of the Earth uniform. There are local mass concentrations – such as mountain ranges - which increase the acceleration due to gravity, and local deficits of mass. In the middle of the oceans the acceleration due to gravity is much weaker because water has only a fraction of the density of the continental crust which makes up the landmasses. The diagram below illustrates the variation in the acceleration due to gravity over the Earth's surface.
is the radius of the earth. The formula above assumes a spherically uniform distribution of mass, this this assumption is only approximately true. The Earth is not a sphere, being flattened at the poles, nor is the density of the Earth uniform. There are local mass concentrations – such as mountain ranges - which increase the acceleration due to gravity, and local deficits of mass. In the middle of the oceans the acceleration due to gravity is much weaker because water has only a fraction of the density of the continental crust which makes up the landmasses. The diagram below illustrates the variation in the acceleration due to gravity over the Earth's surface.
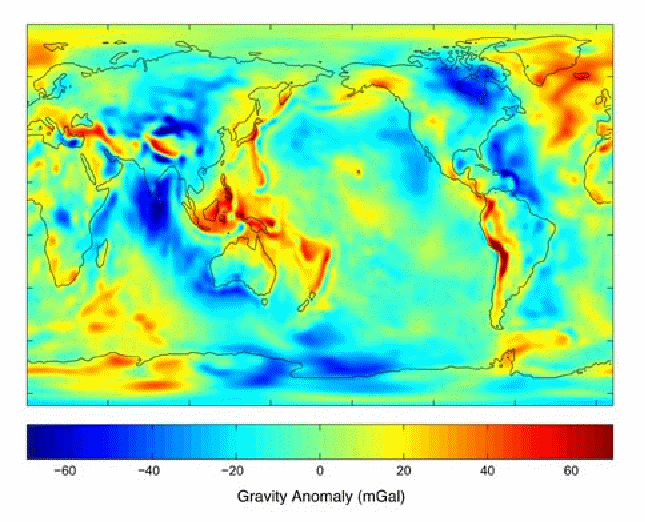
A milligal is a convenient unit for describing variations in gravity over the surface of the Earth. 1 milligal (or mGal) =![]() which can be compared to the total gravity on the Earth's surface of approximately
which can be compared to the total gravity on the Earth's surface of approximately![]() A milligal is about 1 millionth of the standard acceleration on the Earth's surface.
A milligal is about 1 millionth of the standard acceleration on the Earth's surface.
