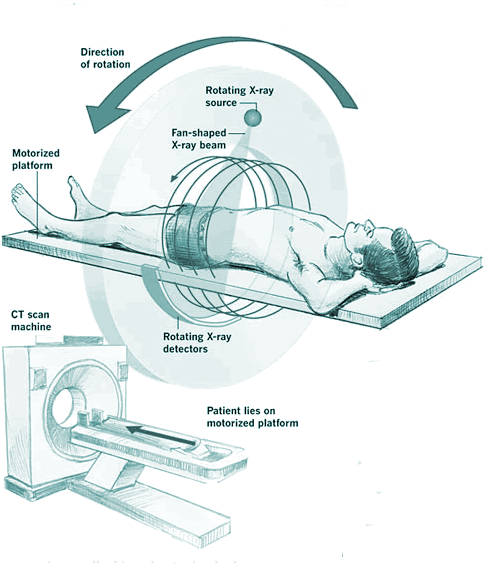
A X ray is a two dimensional image, so parts along the same line of sight from the X ray source is superimposed on each other. This can be overcome by taking X rays at different angles, This is the principle behind 'computerised axial tomography or 'CAT' scan, invented by Geoffry Hounsfield in the UK - I met some who once met his wife (what a tenuous claim to fame).
- The patient lies inside a vertical ring of X ray detectors.
- The X ray tube rotates around the patient, emitting a fan shaped beam of X rays to image the patient from every angle.
- Detectors opposite the X ray tube detect X rays and send signals to a computer which processes them to construct an three dimensional image.
The computer can 'slice' the image into thin slices, and moving pictures viewed of the body's internal structure. This means that tumours can be accurately located and operations can be better planned, and radiography is more accurate.