Often we want to be able vary the voltage across a component – to dim the lights or turn the sound up or down for example. We can do this by varying the resistance in a circuit. The output voltage can be varied with a potential divider shown below. Changing the value of the variable resistor R2 changes the output voltage VOUT .
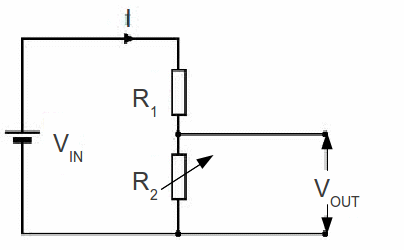
The total resistance in the circuit is![]() so if the battery voltage is
so if the battery voltage is![]() we can use Ohm's Law,
we can use Ohm's Law,![]() to get the current:
to get the current:![]()
Now apply Ohm's law to the output resistor![]() to get the output voltage
to get the output voltage![]()
![]()
If the output resistance R2 is reduced to zero, the output voltage is zero. VOUT can be increased to a maximum by increasing R2 to its largest possible value.
In practice a slightly different arrangement is often used with a sliding contact on a wire.
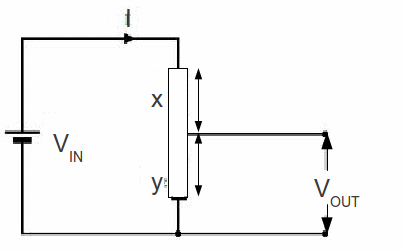
Resistance is proportional to length so![]()
