A parallel sided film can produce an interference pattern as a result of the reflections that take place at both surfaces.
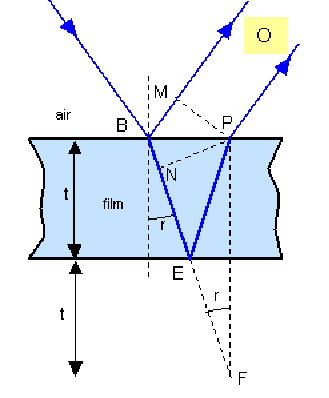
From point B there are two possible paths to the air air the top.
-
Along path BM in air, after reflection at the air – soap interface.
-
Along BNEP in the film, undergoing refraction, refraction, reflection respectively at successive interfaces.
These ray will interfere and the nature of the interference – constructive or destructive – will depend on the optical path difference. The path![]() in air is the same length optically as the length
in air is the same length optically as the length![]() in film, so the path difference is
in film, so the path difference is![]()
The film has a greater refractive index than air so a phase change of![]() occurs at B but none at E.
occurs at B but none at E.
The total optical path difference is then![]()
From the diagram,![]()
If![]() so path difference
so path difference![]() then destructive interference occurs.
then destructive interference occurs.
If![]() then path difference
then path difference![]() then constructive interference occurs.
then constructive interference occurs.
