It consists of two resistors
\[R_1, \: R_2\]
in parallel, with an out taken from contacts across \[V_2\]
.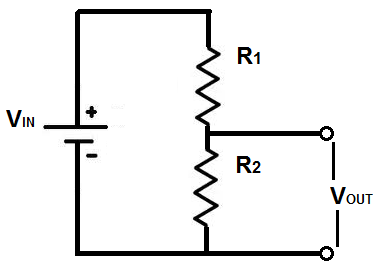
\[V_{OUT}=\frac{R_2}{R_1+R_2} \times V_{IN}\]
.The voltage is split across
\[R_1, \: R_2\]
in the ratio \[R_1 : R_2\]
. One of the resistors can be a variable resistor, then \[V_{OUT}\]
can be adjusted by turning a knob. Such a device is called a potentometer. 