\[y=f(x)\]
, solve \[\frac{d(f(x))}{dx}=0\]
.To classify them, find
\[\frac{d^2 (f(x))}{dx^2}\]
. If \[\frac{d^2 (f(x))}{dx^2} \gt 0\]
at the point, the point is a minimum and if \[\frac{d^2 (f(x))}{dx^2} \lt 0\]
at the point, the point is a maximum. If \[\frac{d^2 (f(x))}{dx^2}=0\]
, the the point is a stationary point of inflexion.Example:
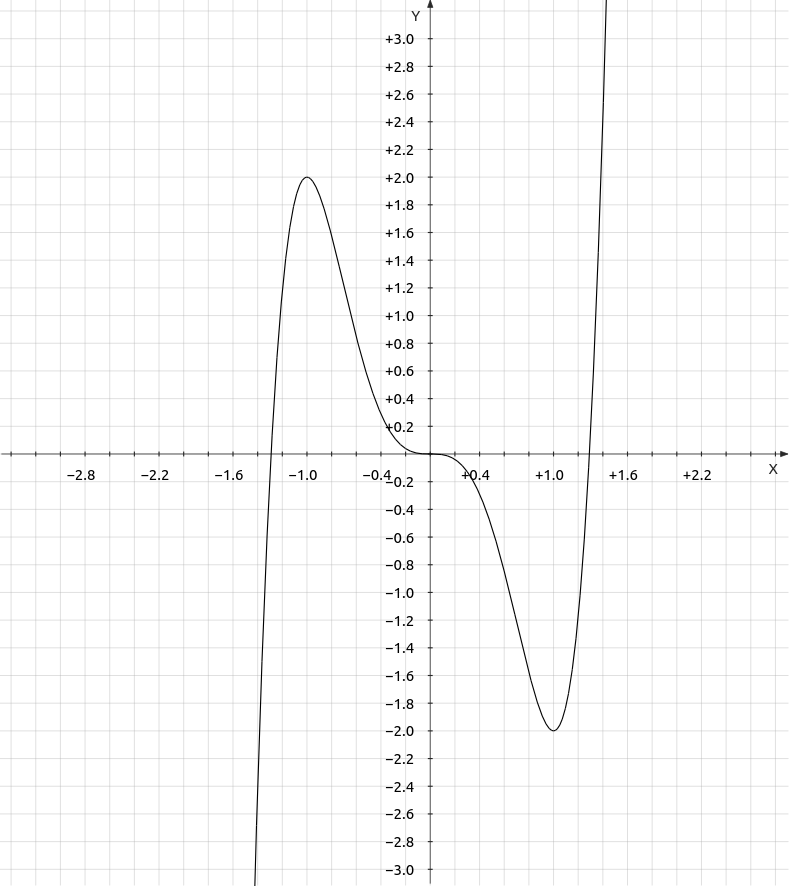
\[f(x)=3x^5-5x^3\]
.\[\frac{d(f(x))}{dx}15x^4-15x^2=0 \rightarrow 15x^2(x^2-1)=0 \rightarrow x=-1, \; 0, \; 1\]
.\[\frac{d^2 (f(x))}{dx^2}=60x^3-30x\]
At
\[x=-1\]
, \[\frac{d^2(f(x))}{dx^2}=-30 \lt 0\]
so this point is a maximum.At
\[x=0\]
, \[\frac{d^2(f(x))}{dx^2}= 0\]
so this point is a stationary point of inflexion.At
\[x=1\]
, \[\frac{d^2(f(x))}{dx^2}=30 \gt 0\]
so this point is a minimum.