Velocity potential is used in fluid dynamics, when a fluid occupies a simply-connected region – no sources or sinks - and is irrotational, so the velocity field![]() has zero curl:
has zero curl:![]()
As a result,![]() can be represented as the gradient of a scalar function:
can be represented as the gradient of a scalar function:
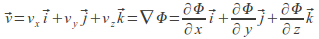 in Cartesian coordinates. Given the velocity field we can find the velocity potential by integration.
in Cartesian coordinates. Given the velocity field we can find the velocity potential by integration.
The velocity potential is not unique. If![]() is a constant then
is a constant then![]() is also a velocity potential for
is also a velocity potential for![]() Conversely, if
Conversely, if![]() is a velocity potential for
is a velocity potential for![]() then
then![]() for some constant
for some constant![]() In other words, velocity potentials are unique up to a constant.
In other words, velocity potentials are unique up to a constant.
Example : Suppose![]() shown below:
shown below:
![]()
Example:![]() Find the velocity potential.
Find the velocity potential.
![]()
![]()
![]()
These are all equal. Put the first and second equal. Then![]() are both functions of
are both functions of![]() only and both are equal to
only and both are equal to![]() which is a function of
which is a function of![]() and
and![]() so
so![]() and
and![]() where
where![]() is an arbitrary constant.
is an arbitrary constant.
