We can estimate the value of the sum of a series of terms![]() by representing the sum by a sequence of rectangles of base 1 and height
by representing the sum by a sequence of rectangles of base 1 and height![]() for
for![]() This can also be estimated using the integral
This can also be estimated using the integral![]()
Then![]() The integral is an underestimate for the sum of the series since since
The integral is an underestimate for the sum of the series since since![]() - we can add a sequence of these expressions to get
- we can add a sequence of these expressions to get![]()
Similarly We can estimate the value of the sum of the series![]() by representing the sum by a sequence of rectangles of base 1 and height
by representing the sum by a sequence of rectangles of base 1 and height![]() for
for![]() This can also be estimated using the integral
This can also be estimated using the integral![]()
Then![]() The integral is an overestimate for the sum of the series since since
The integral is an overestimate for the sum of the series since since![]() - we can add a sequence of these expressions to get
- we can add a sequence of these expressions to get![]()
This is illustrated in the diagram.
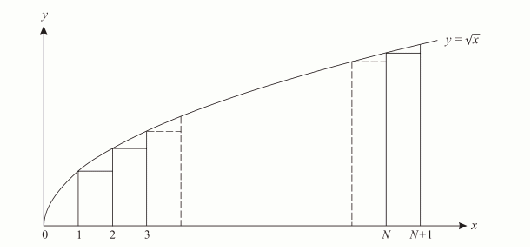
Hence![]()
In general if![]() for
for![]() then
then![]()
and if![]() for
for![]() then
then![]()
