When a charge![]() moves through a potential difference
moves through a potential difference![]() the energy change is
the energy change is![]() If the voltage is constant, then the energy change is proportional to the charge transferred. However, the voltage is not generally constant. When a capacitor is being charged the voltage is increasing. The equation
If the voltage is constant, then the energy change is proportional to the charge transferred. However, the voltage is not generally constant. When a capacitor is being charged the voltage is increasing. The equation![]() obeyed by capacitors implies that the voltage is directly proportional to the charge. If we draw a graph of voltage against charge we obtain a straight line graph through the origin.
obeyed by capacitors implies that the voltage is directly proportional to the charge. If we draw a graph of voltage against charge we obtain a straight line graph through the origin.
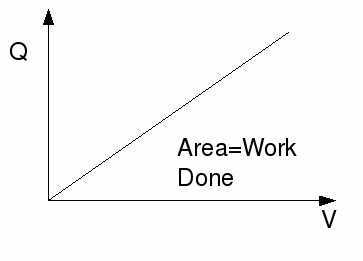
Then the work done in charging the capacitor is equal to the area under the graph is![]()
The energy delivered when a capacitor is being discharged is also![]() for the same reasons.
for the same reasons.
We can show this mathematically. For a charging capacitor at any time,![]() and
and![]() so the work done in transferring a small amount of charge
so the work done in transferring a small amount of charge![]() through a potential difference
through a potential difference![]() is
is![]()
Then![]()
Energy![]() is needed to charge the capacitor but when fully charged the capacitor only stores
is needed to charge the capacitor but when fully charged the capacitor only stores![]() The 'missing' energy is used to overcome resistance in the charging circuit.
The 'missing' energy is used to overcome resistance in the charging circuit.
