Polarisation to some degree occurs whenever light is reflected from a non – conductor of electricity. The degree of polarisation depends on the surface and angle of incidence.
For a particular angle![]() the beam is completely plane polarised as shown below.
the beam is completely plane polarised as shown below.![]() is known as the polarising angle or Brewster angle.
is known as the polarising angle or Brewster angle.
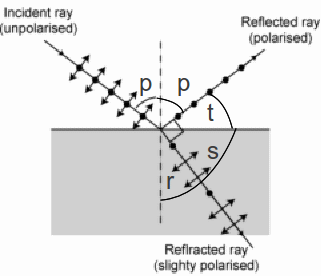
In fact for a material of refractive index n, the Brewster angle p is give by![]() (1)
(1)
It is easily shown that the refracted and reflected beams are at right angles.
From Snell's law we get![]() Substituting for
Substituting for![]() from (1) we get
from (1) we get
![]()
Now![]() so
so![]() hence
hence![]() and similarly
and similarly![]()
Now![]() hence
hence![]()
