The process of radioactive decay has a particular mathematical property. The rate of radioactive decay![]() is proportional to the number
is proportional to the number![]() of undecayed atoms present. We can write
of undecayed atoms present. We can write
![]()
where![]() is the decay rate,
is the decay rate,
![]() is the number of undecayed atoms present
is the number of undecayed atoms present
![]() is the decay constant.
is the decay constant.
We can solve this differential equation using a method called separation of variables:
![]()
To fully solve the original differential equation we have to find![]() When
When![]() the initial number of undecayed atoms. Substituting these into the equation
the initial number of undecayed atoms. Substituting these into the equation![]() gives
gives ![]() Hence
Hence![]()
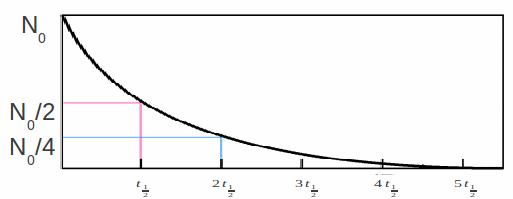
The half life![]() is the time taken for half the atoms to decay ie for
is the time taken for half the atoms to decay ie for![]() to fall to
to fall to![]() We can find
We can find![]()
![]()