Simultaneous equations usually refers to equations of the form
![]() (1)
(1)
![]() (2)
(2)
We solve these be equating the coefficients of![]() or
or ![]() and then eliminating that term. For example, in this case we can multiply (1) by 3 to get
and then eliminating that term. For example, in this case we can multiply (1) by 3 to get
![]() then subtract (2)
then subtract (2)
![]()
![]() and from (1),
and from (1),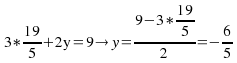
Our problem here is to solve equations such as
![]() (1)
(1)
![]() (2)
(2)
The general approach is to rearrange the linear equation (2) to make![]() the subject say, then substitute the rearranged equation into the quadratic to find a quadratic equation in
the subject say, then substitute the rearranged equation into the quadratic to find a quadratic equation in![]() which we solve to find
which we solve to find![]() then substitute back into the linear equation to find
then substitute back into the linear equation to find![]() For the above example:
For the above example:
![]()
Replace the![]() in
in ![]() with
with ![]() to get
to get![]()
We expand the brackets and simplify this expression:
![]()
We can factorise and solve the last expression.
![]()
If![]() we use (2) to find
we use (2) to find![]() and if
and if![]() we use (1) to find
we use (1) to find![]()
Example:
![]() (1)
(1)
![]() (2)
(2)
Make![]() the subject of (2), then substitute the rearranged equation into (1) to find a quadratic equation in
the subject of (2), then substitute the rearranged equation into (1) to find a quadratic equation in![]() which we solve to find
which we solve to find![]() then substitute this into the (2) to find
then substitute this into the (2) to find![]()
![]()
Replace the![]() in
in ![]() with
with ![]() to get
to get![]()
We expand the brackets and simplify this expression:
![]()
![]() If
If ![]() we use (2) to find
we use (2) to find![]() and if
and if![]() we use (1) to find
we use (1) to find![]()
