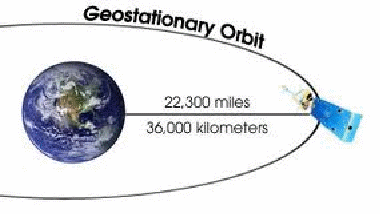
The closer a satellite is to the Earth, the faster it moves. For a certain radius of orbit the satellite will move at such a speed that it is always over the same spot over the Earth's surface – actually above the equator. Such an orbit is called a geostationary or geosynchronous orbit.
We can find the radius of the orbit using, for a circular orbit, centripetal force = gravitational force.
There are equations for each of these forces.
The equation for the centripetal force is![]()
The equation for the gravitational force is![]()
![]() =mass of satellite.
=mass of satellite.
![]() =Mass of Earth.
=Mass of Earth.
![]() =radius of orbit
=radius of orbit
![]()
We can equate these to obtain![]() Simplifying gives
Simplifying gives![]() (1)
(1)
The satellite orbits the Earth, travelling a distance![]() (the circumference of the orbit) in a time
(the circumference of the orbit) in a time![]() The equation
The equation![]() gives
gives![]() hence
hence![]() (2)
(2)
Equation (1) and (2) give![]() and from this we obtain
and from this we obtain![]()
Hence![]()
The radius of the Earth is about 637o km so the satellite is![]() above the Earth's surface.
above the Earth's surface.
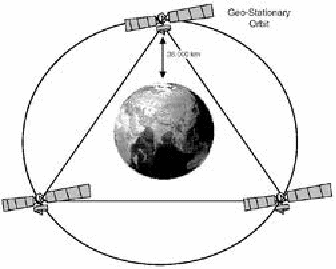
The whole Earth's surface apart from the poles cam be covered using three geostationary satellites, as shown below.