\[A= \int^{x_2}_{x_1} \int^{\gamma_2}_{\gamma_1} dy dx\]
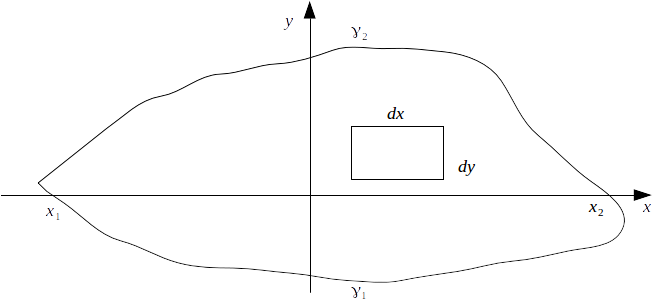
\[\frac{x^2}{a^2} +\frac{y^2}{b^2} =1\]
.For this curve we can take
\[x_1 = -a, x_2 =a, \]
.Rearranging the equation of the ellipse for
\[y\]
gives \[y=\pm b \sqrt{1- \frac{x^2}{a^2}}\]
so we can take \[\gamma21\]
as \[b \sqrt{1- \frac{x^2}{a^2}}\]
and \[\gamma_1\]
as \[-b \sqrt{1- \frac{x^2}{a^2}}\]
The area enclosed by the ellipse is
\[\begin{equation} \begin{aligned} A &= \in^{a}_{-a} \int^{b \sqrt{1- x^2/a^2}}_{-b \sqrt{1- x^2/a^2}} dydx \\ &= \int^{a}_{-a} [y]^{ b \sqrt{1- x^2/a^2}}_{-b \sqrt{1- x^2/a^2}} dx \\ &= 2b \int^{a}_{-a} \sqrt{1- x^2/a^2} dx \\ &= b[x/2 \sqrt{1-x^2/a^2} + a/2 sin^{-1} (x/a)]^a_{-a} \\ &= 2b((0+a/2 sin^{-1} 1 ) - (0-a/2 sin^{-1} -1 )) \\ &= 2b ( \frac{\pi}{2} -(- \frac{\pi}{2})) \\ &= \pi ab \end{aligned} \end{equation}\]
