Stochastic processes model sequences of outcomes such that the outcome or state at each stage depends on previous outcomes or previous states. A typical example is a random walk. At each stage a machine may turn up, down, left or right. If we consider the outcome to be the direction of the movement and the state to be the position of the machine, obviously the position at each stage depends on on the previous position.
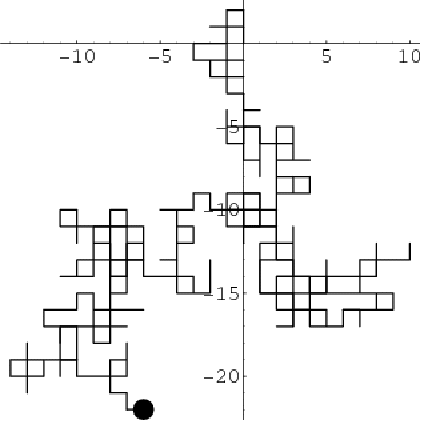
Definition
Let![]() be a subset of
be a subset of![]() A family of random variables
A family of random variables![]() indexed by
indexed by![]() is a stochastic or random process. When
is a stochastic or random process. When![]() or
or![]() is a discrete time process and when
is a discrete time process and when![]() it is a continuous time process.
it is a continuous time process.
When![]() the process is a single event and when
the process is a single event and when![]() is finite the process is a random vector
is finite the process is a random vector![]() x-i in the ith position indicates the ith outcome or state corresponding to
x-i in the ith position indicates the ith outcome or state corresponding to![]() The vector represents the evolution of the system as time passes. When
The vector represents the evolution of the system as time passes. When![]() or
or![]() the changes occur discretely and when
the changes occur discretely and when![]() the changes may occur at any instant.
the changes may occur at any instant.
