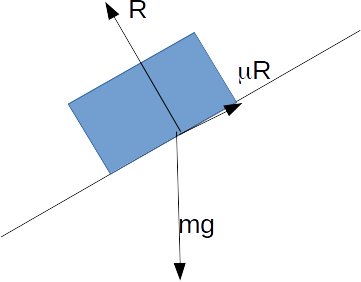
\[R\]
for a body resting on a smooth surface is perpendicular to the surface. For a surface that is not smooth we can consider the reaction force to consist of two components: a normal component \[R\]
, perpendicular to the surface, as for a smooth surface, and a friction component, \[Fr\]
tangential to the surface.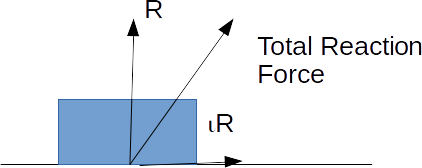
\[\sqrt{R^2 +Fr^2}\]
.If the body is on the point of slipping, the friction force is equal to
\[\mu R\]
where \[\mu\]
is the coefficient of friction. Th magnitude of the contact force is then \[\sqrt{R^2+(\mu R)^2} = R \sqrt{1_ \mu^2}\]
.(1)For a body at rest in limiting equilibrium or moving with a constant velocity, there is no net force and the magnitude of the total reaction force is (1) above.
If the particle is at rest on a slope, the total con-act force must be in opposition to the force of gravity i.e. it must be vertically up.