\[\alpha\]
. We enclose a section of the plate within a closed cuboid and apply Gauss's Law to the surface.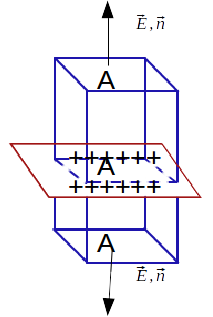
\[\int_S \mathbf{E} \cdot \mathbf{n} dS = \frac{q}{\epsilon_0}\]
where
\[q\]
is the charge enclosed by the surface.\[\mathbf{E}\]
is constant and perpendicular to the surface of the plate. This means that at the sides of the surface the normal \[\mathbf{n}\]
is at right angles to the electric field \[\mathbf{E}\]
. The only contributions to the surface integral comes from the surfaces of the cuboid parallel to the plate.
\[\int_S \mathbf{E} \cdot \mathbf{n} dS = \frac{q}{\epsilon_0} \rightarrow 2 AE = \alpha A \rightarrow E =\frac{A \alpha}{\epsilon_0} \rightarrow E = \frac{\alpha}{2 \epsilon_0}\]
