If we have two populations with population statistics![]() and
and![]() thenthe mean difference between the means of two samples is
thenthe mean difference between the means of two samples is![]() andif the sample sizes are
andif the sample sizes are![]() and
and![]() (frompopulations 1 and 2 respectively) are large, then difference betweenthe sample means is normally distributed:
(frompopulations 1 and 2 respectively) are large, then difference betweenthe sample means is normally distributed:![]() (fromthe central limit theorem).
(fromthe central limit theorem).
When the sample sizes are small we need to make the additionalassumptions
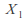 and
and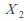 arenormally distributed
arenormally distributedThe samples are independent
The variances of the populations are equal
In practice the sample variances can be very dissimilar, but theequality of the population variances can be tested using the F –test.
In general we do not know the population variances and mustcalculate estimates for the population variances,![]() and
and![]() Ifwe assume
Ifwe assume![]() and
and![]() arenormally distributed then we can use an estimator for commonvariance
arenormally distributed then we can use an estimator for commonvariance![]() and the difference between the means of the two samples is has a t –distribution with
and the difference between the means of the two samples is has a t –distribution with![]() degreesof freedom
degreesof freedom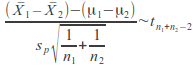
Example: A sample of the heights of boys and girls is taken andthe following results are obtained. Conduct a hypothesis test thatboys are 3 cm taller than girls.
Boy's heights: 153, 149, 148, 158, 159, 141, 142, 145
Girl's heights: 143, 147, 133, 126, 139, 132, 143
![]() and
and![]()
![]()
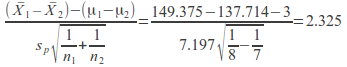
This is greater than![]() sothere is evidence to reject the null hypothesis that
sothere is evidence to reject the null hypothesis that![]() Boysare more than three cm taller than girls.
Boysare more than three cm taller than girls.
