A thermistor is an electronic device that responds to temperature by lowering its electrical resistor. The transistor can be used in a circuit to switch on a fire alarm.
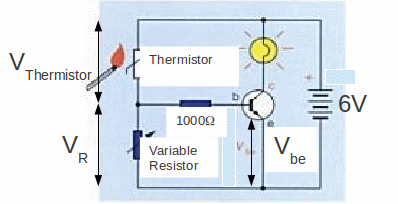
When a fire is lit, the thermistor gets hotter and the resistance of the thermistor decreases. The voltage across the thermistor goes down according to the potentiometer equation![]()
The voltage across the thermistor will fall resulting in a corresponding increase in the voltage across the variable resistor and the base – emitter voltage![]() across the transistor. When the base emitter voltage rises above a certain level – about 0.6 V - the transistor will act as an amplifier, switching on. When the base emitter voltage is above about 1.5V the transistor is fully on. The above circuit can be used as a fire or heat alarm. Swapping thermistor and variable resistor, and changing the resistance of the variable resistor to a suitable value can make the circuit operate as a frost alarm, detecting when the temperature is too low.
across the transistor. When the base emitter voltage rises above a certain level – about 0.6 V - the transistor will act as an amplifier, switching on. When the base emitter voltage is above about 1.5V the transistor is fully on. The above circuit can be used as a fire or heat alarm. Swapping thermistor and variable resistor, and changing the resistance of the variable resistor to a suitable value can make the circuit operate as a frost alarm, detecting when the temperature is too low.
