\[\]
lows us to classify turning points of a function \[f(x)\]
(points for which \[\frac{df}{dx}=0\]
).Suppose there is a function
\[f(x)\]
and that at some point \[x_0\]
, \[\frac{df}{dx}=0\]
.Then
\[(x_0, f(x_0))\]
is a turning point of the function \[f(x)\]
andIf
\[\frac{d^2f}{dx^2} < 0\]
then \[(x_0, f(x_0))\]
is at a maximum for the function \[f(x)\]
.If
\[\frac{d^2f}{dx^2} > 0\]
then \[(x_0, f(x_0))\]
is at a minimum for the function \[f(x)\]
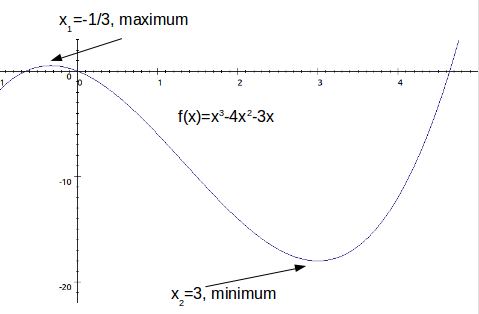
.Example: Let
\[f(x)=x^3-4x^2-3x\]
. Then \[\frac{df}{dx}=3x^2-8x-3\]
.
Ti find the turning point set \[\frac{df}{dx}=3x^2-8x-3=(3x+1)(x-3)=0\]
.Then the turning points are
\[x_1 =- \frac{1}{3}, \: x_2 =3\]
.\[\frac{d^2f}{dx^2}=6x-8\]
.When
\[x=- \frac{1}{3}, \: \frac{d^2f}{dx^2}=6 \times - \frac{1}{3}-8=-10 \lt 0\]
.Hence
\[x_1= - \frac{1}{3}\]
is at a maximum.When
\[x=3, \: \frac{d^2f}{dx^2}=6 \times 3-8=10 \gt 0\]
.Hence
\[x_1= - \frac{1}{3}\]
is at a minimum.