\[(x_0, f(x_0))\]
is a point of inflexion on a curve \[f(x)\]
if \[\frac{d^2f}{dx^2} \|_{x=x_0}=0\]
.If also
\[\frac{df}{dx} \|_{x=x_0}=0\]
the point is a horizontal point of inflexion.Example:
\[f(x)=x^3(x-1)=x^4-x^3\]
.\[\frac{df}{dx}=4x^3-3x^2\]
so \[\frac{df}{dx}=0\]
at \[x=0\]
\[\frac{d^f}{dx^2}=12x^2-6x\]
so \[\frac{d^2f}{dx^2}=0\]
at \[x=0\]
.The point
\[(0,f(0))=(0,0)\]
is a stationary point of inflexion.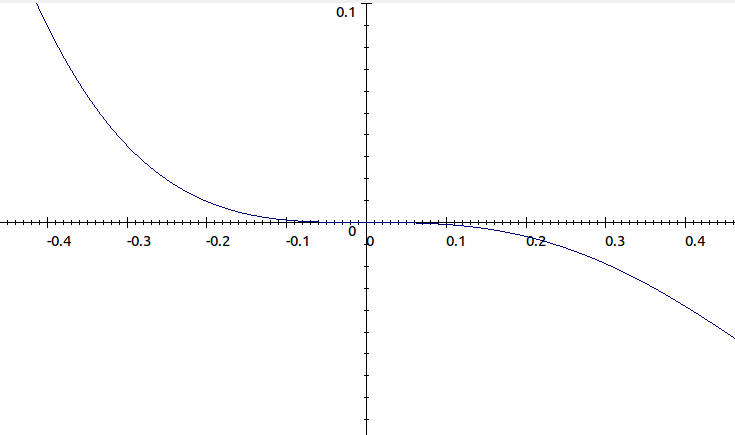
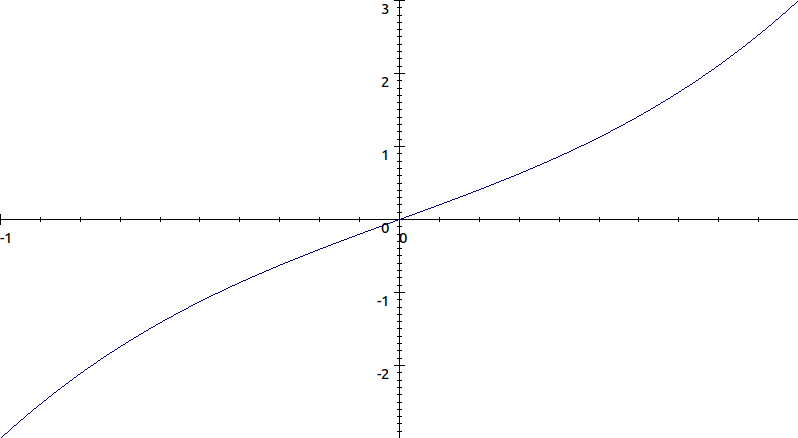
\[f(x)=x(x^2+2)=x^3+2x\]
.\[\frac{df}{dx}=3x^2+2, \: \frac{d^2f}{dx^2}=6x\]
.When
\[x=0\]
, \[\frac{df}{dx} \neq 0, \: \frac{d^2f}{dx^2} = 0\]
.When
\[x=0\]
, the point is a point of inflexion but not a stationary point of inflexion.