The separation of variables method is a technique for solving partial differential equations subject to boundary conditions and is used to solve problems where
-
The partial differential equation to be solved is linear and homogeneous.
-
The boundary conditions are of the form
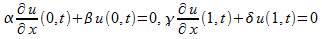 where
where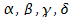 are constants.
are constants. -
The solution obeys the initial condition
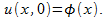
I will illustrate the method with an example.
![]() (1)
(1)
![]()
![]()
We look for solutions of the form![]()
Substitution into the original differential equation gives![]() Divide by
Divide by![]() to gives
to gives![]() The left hand side is a function of t only and the right hand side is a function of x only. Since x and t are independent variables, we must have that both sides are constant. Suppose that both sides equal k. We can write
The left hand side is a function of t only and the right hand side is a function of x only. Since x and t are independent variables, we must have that both sides are constant. Suppose that both sides equal k. We can write
![]() and
and![]() or
or![]() (2)
(2)
If![]() the solution to the first is
the solution to the first is![]() This solution tends to infinity as
This solution tends to infinity as![]() tends to infinity so we must have
tends to infinity so we must have![]() Put
Put![]() then the two equations (2) become
then the two equations (2) become![]() with solutions
with solutions![]() so all solutions take the form
so all solutions take the form![]() since
since![]() are arbitrary. We now fit these solutions to the boundary conditions.
are arbitrary. We now fit these solutions to the boundary conditions.
![]()
![]()
Since the original equation is linear, any linear combination of these solutions is also a solution. We can write the most general solution to (1) as![]()
We now fit these solutions to the initial condition![]()
![]()
In general fitting the most general solution![]() to the initial condition will involve finding the coefficients of a Fourier series.
to the initial condition will involve finding the coefficients of a Fourier series.
