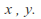A metric space is a set of points where the distance between any two points![]() can be calculated with a function of the coordinates of the points, called a metric:
can be calculated with a function of the coordinates of the points, called a metric:![]()
The metric space which most closely corresponds to our intuitive understanding of space is the ordinary Euclidean space, in one, two, three of more dimensions. In fact, the notion of "metric" is a generalization of the Euclidean metric, which defines the distance between two points as the length of the straight line segment connecting them.
The geometric properties of the space depend on the metric chosen, and by using a different metric we can construct non-Euclidean geometries such as those used in the theory of general relativity.
The metric must satisfy three properties:
M1: If![]() then
then![]() If
If![]() then
then![]()
M2:![]() The distance between two points is a number which does not depend on how the points are oriented.
The distance between two points is a number which does not depend on how the points are oriented.
M3:![]() where
where![]() are any three points in the space. This is a generalization of the triangle inequality.
are any three points in the space. This is a generalization of the triangle inequality.
Examples:
-
The real numbers with the metric
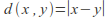 which returns the magnitude of the difference between two numbers.
which returns the magnitude of the difference between two numbers.
-
If
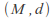 is a metric space and
is a metric space and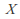 is a subset of
is a subset of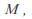 then
then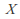 becomes a metric space by restricting
becomes a metric space by restricting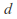 to
to  .
.
-
The discrete metric, where
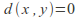 if
if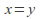 and
and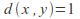 is a metric. Any non empty set can be made into a metric space with this metric. Any point in the space is an open ball, and therefore every subset is open and the space has the discrete topology.
is a metric. Any non empty set can be made into a metric space with this metric. Any point in the space is an open ball, and therefore every subset is open and the space has the discrete topology.
-
If
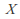 is some set and
is some set and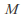 is a metric space, then the set of all bounded functions
is a metric space, then the set of all bounded functions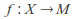 (i.e. those functions whose image is a bounded subset of
(i.e. those functions whose image is a bounded subset of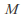 ) can be turned into a metric space by defining
) can be turned into a metric space by defining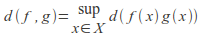 for any two bounded functions
for any two bounded functions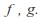 Here sup is the supremum.
Here sup is the supremum.
-
If
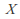 is a topological (or metric) space and
is a topological (or metric) space and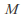 is a metric space, then the set of all bounded continuous functions from
is a metric space, then the set of all bounded continuous functions from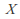 to
to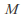 forms a metric space if we define the metric as above:
forms a metric space if we define the metric as above: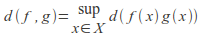 for any two bounded continuous functions
for any two bounded continuous functions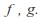 If
If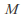 is complete, then this space is complete as well.
is complete, then this space is complete as well.
-
The set V of vertices of an undirected graph G can be turned into a metric space by defining
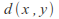 to be the length of the shortest path connecting the vertices
to be the length of the shortest path connecting the vertices