Newton – Cotes formulae use interpolating polynomials to![]() to evaluate
to evaluate![]() using leading to the formula
using leading to the formula![]() where the
where the![]() are equally spaced, so
are equally spaced, so![]()
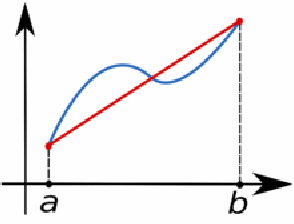
The simplest example of this method is the trapezium rule. It calculates the area of the trapezium formed by approximating![]() using linear interpolation. This is shown below for
using linear interpolation. This is shown below for![]() that interpolates only
that interpolates only![]() and
and![]()
![]()
The trapezium rule can be obtained by integrating the linear interpolation function
![]() over the interval
over the interval![]()
We can generate other integration rules by using higher order Lagrange polynomials.
![]()
The![]() are labelled
are labelled![]() and called weights, thus we obtain
and called weights, thus we obtain![]()
Closed Newton – Cotes formulae include the endpoints![]() and
and![]() in the interpolating polynomial.
in the interpolating polynomial.
